It is categorized as either gonococcal or nongonococcal. The main difference is that the gonococcal type is caused by the spread of the gonorrhea bacteria and nongonococcal infections are not. You don’t need to wait until your knee problem has completely gone to do this. If you have a job, it’s important to continue working if you can. Speak to your employer about any practical help they can offer.
If you’re experiencing severe knee pain, talk to your doctor to find out what’s causing it. Some knee conditions can be diagnosed based on a physical examination alone. Your provider may use additional tests to confirm a diagnosis and determine the best treatments. The key to proper treatment is finding out what causes your knee pain. Then your healthcare provider can form the right treatment plan for you. A lot of things can cause pain in your knee(s), including medical conditions, trauma, and injuries from putting too much pressure on the joint.
That’s why it’s one of the most commonly injured joints. Knee pain can be a temporary, short-term problem, but it can also be a chronic (long-term) issue that needs diagnosis and treatment by a healthcare provider. Knee pain is a common complaint that affects people of all ages.
What is Joint in Knee Pain?
But your provider may suggest it if the pain is severe and other treatments haven’t helped. You might need surgery to repair a damaged ligament, bone fracture or if you have severe arthritis. Your provider might suggest physical therapy if you have arthritis or are recovering from an injury. A physical therapist will show you stretches and exercises that strengthen the muscles around your affected knee.
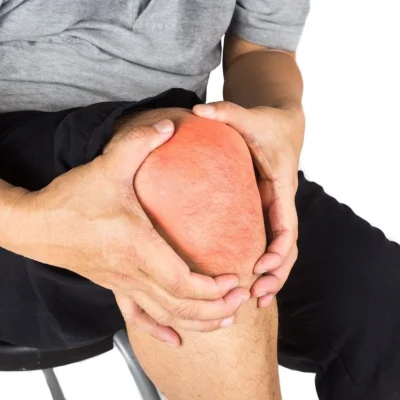
Joint in knee pain refers to the discomfort or inflammation experienced in the joint of the knee. This condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, overuse, arthritis, or other medical conditions.
The concentration of platelets in the new mixture can be 5 to 10 times richer than in normal blood. Researchers say the shots promote healing and lessen inflammation, which should reduce pain and swelling. Cardio exercises strengthen the muscles of the heart, but not the joints. It is weight training mixed with keeping your muscles limber.
Carrying extra body weight makes it more likely that you will get joint pain in the first place. If you have joint pain already, being overweight can make it worse. Losing even a small amount of weight can make a big difference to knee pain. If you’re dealing with symptoms of pain that won’t subside or a joint that locks up, don’t ignore them.
Synovial fluid serves as a lubricant for your joints. When it becomes thicker, joint tissues may rub against each other more, leading to pain. The exact reason why your joints hurt when it’s cold isn’t known. What exactly is the connection between cold weather and joint pain?
Causes of Joint in Knee Pain:
- Arthritis – Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis
- Injury – Sprains, strains, tears
- Overuse – Repetitive movements or activities
- Medical conditions – Bursitis, tendonitis
Treatments for Joint in Knee Pain:
- Rest and ice
- Physical therapy
- Medications – NSAIDs, corticosteroids
- Injections – Cortisone injections
- Surgery – Arthroscopic surgery, knee replacement
Frequently Asked Questions about Joint in Knee Pain:
Q: Can joint in knee pain be prevented?
A: While some causes of joint in knee pain cannot be avoided, such as arthritis, injury prevention strategies can help reduce the risk of developing this condition.
Q: When should I see a doctor for joint in knee pain?
A: If the pain is severe, persistent, or affecting your daily activities, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.