Some people find relief by rubbing the affected knee with creams containing a numbing agent, such as lidocaine, or capsaicin, the substance that makes chili peppers hot. Most cases of the disease begin when a person is 16–35 years old. Still’s disease is a rare inflammatory disorder that has a prevalence of 1–34 cases per 1 million people.
In severe cases, a person may experience a complete tear of the tendon. The quadriceps tendon is above the knee cap and connects the quadriceps muscles to the top of the knee. The hamstrings are tendons that attach the hamstring muscles to the pelvis, knee, and lower leg. When a person stretches or overuses the hamstring tendons, they may notice some swelling and pain at the back of the thigh.
Patellar tendinopathy, or jumper’s knee, happens when the patellar tendon develops small tears. Jumpers tend to experience this type of knee pain as jumping puts stress on the patellar or quadriceps tendon. Athletes prone to IT band syndrome include basketball players, long-distance runners, and soccer players. A person with IT band syndrome tends to feel pain at the side of the knee. The location of the pain can sometimes help a doctor diagnose the issue.
“Meniscal injuries can occur with a degenerative type of pattern but also traumatic or athletic events.” Meniscus tears are common with any activity where you twist or turn your knee suddenly, such as playing pickleball or tennis. The decision to try knee injections should be made in concert with a knowledgeable doctor and with the understanding that they may not work. In the next few years, researchers predict that more effective knee injections and effective regenerative injections will likely be refined or discovered. In this process, stem cells are extracted from bone marrow or fat, then injected into an arthritic knee. Theoretically, the stem cells will promote tissue regeneration in the joint, though laboratory tests have shown that few stem cells survive or remain in the joint after being injected.
It is an auto-inflammatory disease, in which the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues. In the case of knee pain, RA attacks the tissues of the knee. The knee joint is complex, and a range of factors can lead to damage and pain. The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the key ligaments that help stabilize the knee joint. The ACL connects the thighbone (femur) to the shinbone (tibia).
Therefore, consideration should be given to examining and tailoring treatments to both knee regions in patients with combined knee pain pattern. Additionally, patellofemoral pain may be as likely a cause of symptoms and functional limitation as tibiofemoral pain in older adults with chronic knee pain. Further research to develop and validate effective approaches that specifically address patellofemoral pain in older adults with chronic knee pain may be warranted. Interestingly, these percentages were comparable to those reported by patients with tibiofemoral only pain. This finding suggests that pain arising from the patellofemoral region may be as important as tibiofemoral pain in influencing a patient with chronic knee pain to seek medical care.
But since then, both research and experience have proven me wrong. If you’ve followed me for a while – then you know one of my favorite sayings is “mobility before stability”. That’s because a joint that moves fully and freely feels and functions better – and allows the muscles around that joint to work at their best. Too often, people mistakenly look at muscular strength first as the solution to solving pain, when they should be looking a bit deeper. Regarding knees, you need a bit of what we call “hyper-extension”. But most practitioners tend to focus only on how well a knee is bending.
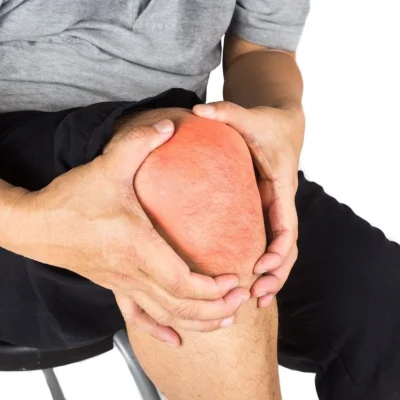
Chronic pain in the knee joint can be a debilitating condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, arthritis, overuse, or other medical conditions.
Causes of Chronic Pain in Knee Joint
There are several common causes of chronic pain in the knee joint:
- Injury: A past injury to the knee, such as a torn ligament or meniscus, can lead to chronic pain.
- Arthritis: Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or other types of arthritis can cause chronic inflammation and pain in the knee joint.
- Overuse: Excessive strain on the knee joint from activities like running, jumping, or repetitive movements can lead to chronic pain.
Treatment Options for Chronic Pain in Knee Joint
There are several treatment options available for chronic pain in the knee joint:
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening exercises and stretches can help improve flexibility and reduce pain.
- Medication: Over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers can help manage pain and inflammation.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections or hyaluronic acid injections can provide temporary relief for knee pain.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Q: Can chronic pain in the knee joint be cured?
- A: While chronic pain in the knee joint may not always be fully cured, it can often be managed effectively with proper treatment and lifestyle changes.