Knee pain is so common that almost everyone’s felt it in their lives. But that doesn’t mean you have to live in constant pain. Visit a healthcare provider if knee pain is making it bad enough to make you change your daily routine. They’ll help you find treatments that get you back to what you love. But your provider may suggest it if the pain is severe and other treatments haven’t helped. You might need surgery to repair a damaged ligament, bone fracture or if you have severe arthritis.
You might feel pain every once in a while, but don’t ignore it if it’s been more than a few days in a row since you’ve been pain-free. For example, you might feel pain when you’re moving or bending your knee which gets better when you rest. Some people also feel pain at different parts of the day. You could feel more pain first thing in the morning when you wake up.
It can happen suddenly after your leg is sharply twisted during sports or exercise. A tear might also occur as a result of aging-related wear and tear. Knee pain may be felt on the inner or outer side of the knee joint depending on which tissues or structures are affected.
Tendons are tough bands of tissue that connect muscles to bones. When you overdo exercise, they can become inflamed and sore. You may also hear it called “jumper’s knee” because repetitive jumping, such as from basketball, is the most common cause. In addition to the traditional medical treatments mentioned above, you may also benefit from mental health counseling to cope with the impacts of living with chronic pain. Staying engaged in low-impact exercise and accessible hobbies that bring you joy and meaning are also important.
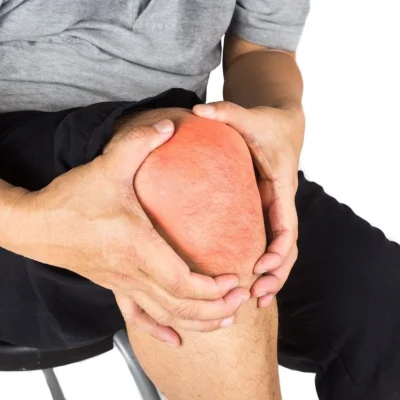
**Inflammation** and **pain** in the knee often go hand in hand, causing discomfort and hindering daily activities for many individuals. **Inflammation** is the body’s natural response to injury or infection, but when it becomes chronic, it can lead to persistent pain and stiffness in the knee joint.
It causes sudden, intense bouts of pain in the joints along with swelling, redness, tenderness, and heat. Joints are places in your body where two bones meet. Your knee joint connects your thigh to your lower leg. It’s where your thigh bone (femur) meets your shin bone (tibia). Notably, people with endometriosis frequently describe their pain as “radiating” from the pelvis down the lower limbs.
Treatment will depend on what is causing your hip pain so it’s important to get a proper diagnosis. They’re regarded as the fire extinguisher of knee injections — they usually start working within 48 hours to reduce pain and inflammation around the knee joint. Studies show corticosteroids can effectively provide short-term relief, though some people report success over a longer period. About 1 in 7 people diagnosed with knee osteoarthritis will receive some sort of injection to treat the painful, sometimes debilitating, symptoms of the disease. Most people who experience knee swelling don’t need surgery.
But most often, knee bursitis happens over the kneecap or on the inner side of the knee below the joint. While there are more than 100 types of arthritis, osteoarthritis (OA) is the one that most often affects the knee. OA is also most likely in adults over 50 years of age and is known as a “wear-and-tear” type of arthritis, where joint damage occurs from knee cartilage breaking down. When there are problems that affect joints, or the areas where bones meet together, you may experience pain along with other symptoms like swelling and stiffness.
Causes of Inflammation and Pain in the Knee
There are several factors that can contribute to **inflammation** and **pain** in the knee. Common causes include **arthritis**, **overuse injuries**, **ligament tears**, **meniscus tears**, and **bursitis**. **Arthritis**, in particular, is a leading cause of chronic knee **inflammation** and **pain**, as the cartilage in the joint wears down over time, causing the bones to rub against each other.
Symptoms of Inflammation and Pain in the Knee
Individuals experiencing **inflammation** and **pain** in the knee may notice symptoms such as swelling, redness, warmth, and stiffness in the joint. They may also experience a limited range of motion and difficulty bearing weight on the affected knee. It is important to seek medical attention if these symptoms persist, as untreated **inflammation** can lead to further damage and worsening **pain** in the knee.
**Treatment** options for **inflammation** and **pain** in the knee may include rest, ice, compression, elevation (**RICE**), physical therapy, medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (**NSAIDs**), corticosteroid injections, and in severe cases, surgery. It is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the underlying cause of **inflammation** and **pain** in the knee.