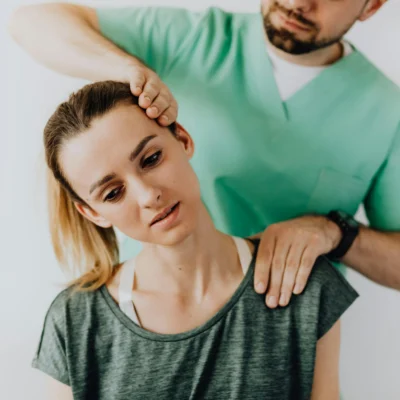
But while the causes of knee pain may vary (from arthritis and tendinitis to a strain or sprain), movement can be an effective way to minimize your symptoms. At the initial visit, the physical therapist will evaluate your knee pain and develop a customized treatment plan. Physical therapy for the knees involves exercises, hands-on therapy, and treatments like ultrasound.
Knee pain is a common issue that can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Whether it is caused by injury, arthritis, or overuse, finding relief from this discomfort is crucial for maintaining mobility and overall well-being. One effective way to address knee pain is through physical therapy.
This is where the notion of “bone on bone” comes from, but Dr. Peterson advises against dwelling on it. How you feel and function is more important than what your X-rays show, he says. And what your scans say isn’t a reliable indicator of how you feel in your everyday life.
Your provider will tell you which type of brace you’ll need and how often you should wear it. Most people can take over-the-counter NSAIDs (ibuprofen, aspirin and naproxen) or acetaminophen (Tylenol®). Don’t take these medications for more than 10 days in a row without talking to your provider or if you have kidney or liver disease.
Knee pain can be tricky to figure out – especially if it’s chronic. The key to successfully getting rid of knee pain starts with correctly identifying the cause. And from my experience – arthritis, age, and wear and tear serve as “excuses” when a practitioner doesn’t know where to look.
The Role of Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a vital role in the treatment of knee pain by focusing on strengthening the muscles surrounding the knee joint, improving flexibility, and promoting proper alignment and movement patterns. Through targeted exercises and interventions, physical therapists aim to reduce pain, improve function, and prevent future injuries.
Two rings of cartilage (the medial and lateral meniscus), attached to the shin bone (tibia), also act as shock absorbers for the knee. When this protective cartilage gradually wears away over time, osteoarthritis develops — causing pain and swelling in the knee. The best exercise for knee pain is the one you feel capable and comfortable doing. The specific injury or underlying condition you’re trying to improve also plays a significant role. If you are suffering from knee pain that ranges from mild to moderate pain, then you will want to seek medical advice before hitting the gym.
Benefits of Physical Therapy for Knee Pain
- Improved strength and stability: Physical therapy helps strengthen the muscles supporting the knee, which can help alleviate pain and prevent further damage.
- Enhanced range of motion: By incorporating stretching and mobility exercises, physical therapy can improve flexibility and joint function.
- Pain management: Therapeutic modalities such as ultrasound, electrical stimulation, and ice therapy can help reduce pain and inflammation in the knee.
- Individualized treatment: Physical therapists tailor treatment plans to each patient’s specific needs and goals, ensuring a personalized approach to care.
Frequently Asked Questions about Physical Therapy for Knee Pain
- How long does it take to see results from physical therapy? – The timeline for improvement varies depending on the severity of the knee pain and the individual’s response to treatment. However, many patients experience relief within a few weeks of starting therapy.
- Is physical therapy painful? – While some discomfort may be experienced during certain exercises, physical therapy is designed to alleviate pain and improve function in the long run.
- Can physical therapy prevent surgery for knee pain? – In some cases, physical therapy can help individuals avoid the need for surgery by addressing underlying issues and improving overall knee health.
In conclusion, physical therapy is a valuable and effective tool for managing knee pain. By working with a skilled physical therapist, individuals can improve their strength, flexibility, and function, ultimately leading to a reduction in pain and an improved quality of life.