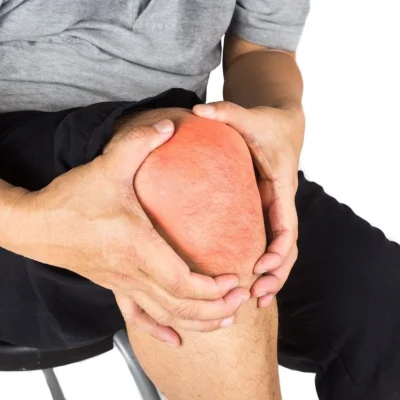
Knee pain can be a frustrating and debilitating condition that affects people of all ages. Whether you’re an athlete dealing with a sports injury or an older individual experiencing arthritis, finding relief from knee pain is crucial for maintaining your quality of life.
It can cause swelling, pressure, and discomfort in the knee. Kneeling knee pain may also result from other conditions related to the knee itself. Knee pain when kneeling can be due to a number of conditions, such as bursitis, arthritis, and patellar tendonitis. While activity during the day contributes to the pain you feel in your knees at night, so does the fact that you’ve actually slowed down enough to notice. A person can contact a doctor when their knee pain does not go away within a few weeks.
Causes of Knee Pain
Simple causes of knee pain often clear up on their own while you take steps to manage your symptoms. If knee pain is caused by an accident or injury, you should contact your health care provider. Each bone end is covered with a layer of cartilage that absorbs shock and protects the knee. Basically, the knee is 2 long leg bones held together by muscles, ligaments, and tendons. A bursa is a sac that holds a small amount of fluid that’s under the skin above your joint. Overuse, falls, or repeated bending and kneeling can irritate the bursa on top of your kneecap.
There are several common causes of knee pain, including **injury**, **overuse**, **arthritis**, **meniscus tears**, and **ligament sprains**. **Injuries** such as **torn ligaments** or **cartilage damage** can result in acute knee pain, while chronic conditions like arthritis can cause persistent discomfort and stiffness.
Injury can damage the surrounding tissue and joints. You can tear or strain the medial collateral ligament or meniscus. You can usually treat knee pain at home by taking a break from physical activities and taking over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers. Visit a healthcare provider if you’re feeling pain that’s bad enough to affect your daily routine or that’s making it hard to move. See a provider if you experience knee pain that lasts more than a few days without getting better. Treating this knee pain is all about pain management and what you can do to reduce the stress on those joints.
Treatments for Knee Pain
When it comes to treating knee pain, there are a variety of options available depending on the underlying cause. **Physical therapy** can help improve strength and flexibility in the muscles surrounding the knee, while **medications** like **anti-inflammatories** can help reduce pain and swelling. In more severe cases, **surgery** may be required to repair damaged tissues or realign the joint.
The most common cause of bursitis is putting too much pressure on your knee, such as by kneeling or squatting without wearing knee pads or braces for support. Sometimes, a bursa can become inflamed after you hit your knee during an injury. Knee sprains and knee ligament tears are similar injuries.
They’re usually made of stiff plastic or metal with cushions and straps that wrap around your knee and leg. Your provider will tell you which type of brace you’ll need and how often you should wear it. “It would have been beneficial to study other chronic inflammatory pain disorders and see if they would come to the same conclusion,” Mikhael said.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional if you’re experiencing knee pain, as they can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend the most effective treatment plan for your specific condition. By addressing knee pain promptly, you can prevent further damage and improve your overall quality of life.
Knees are one of the most commonly injured joints, and sprains are a common injury. They happen when something forces ligaments in your knee to stretch too far or tear. Sports injuries and falls cause most sprained knees. You’ll probably be able to manage your symptoms with at-home treatments, but you should visit a healthcare provider to get the injury diagnosed. Knee pain is caused by injury and a variety of medical conditions. Fixing your knee pain starts with figuring out what is causing it and then following the right treatment plan.
Usually rest, ice, and OTC pain medication, along with stretching and strengthening exercises, will relieve this knee pain with time. Bursitis can cause painful swelling over your kneecap or at the side of your knee. In your knee, there are small sacs of fluid that help allow tendons to glide smoothly over your joints. In bursitis, these sacs of fluid get irritated and swell, which puts pressure on the adjacent parts of the knee, causing pain. Visit a healthcare provider if you’ve experienced an injury and have knee sprain symptoms. Talk to your provider if your symptoms aren’t improving after a few days of treatment (or if they’re getting worse).