The SI joint is where the tailbone (sacrum) connects with the back of the pelvis (ilium). Issues in this area can cause pain that radiates down the back of the legs. To understand the causes of pain that radiates from the hips down the legs, it’s important to first understand the joints in this area of the body. As the joint degrades, a person may notice more swelling and inflammation in their knee. If these symptoms reduce a person’s ability to stay mobile, they may also develop muscle weakness. People who engage in sports with a lot of jumping, such as basketball players, have a higher risk of quadricep tendon injury.
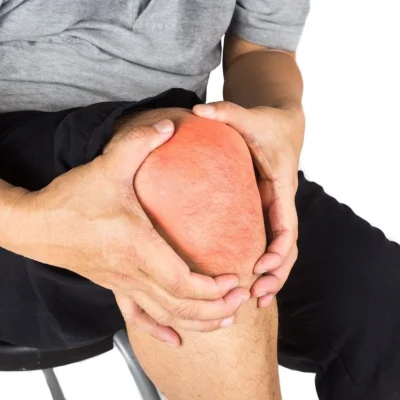
Chronic knee pain can be debilitating and greatly impact one’s quality of life. There are several common reasons why individuals may experience ongoing discomfort in their knees.
Injury
One of the key roles of the knee is to support the body weight, and with every step, it puts huge pressure on the knees. Chronic knee pain can occur due to overuse injury in which the muscle, tendon, or ligament is damaged. Chronic knee pain is also a result of osteoarthritis that comes with aging. The fibrous tissues that lie between the knee bones become thin and brittle and can tear easily with increasing age. The cartilage also starts to disappear, causing bone pain in older people. Such movement can actually help keep your tendons limber and can circulate fluid that helps lubricate and protect your knee joints.
A meniscus tear is a common injury that typically requires surgery to repair. Unlike a ligament injury, which can develop in a variety of ways, a meniscus tear is usually caused by a single movement, such as an abrupt twist or turn. Corticosteroid injections are also a possibility for managing pain in your knee from arthritis.
Post-traumatic arthritis develops after an injury to the knee. Meniscus tears and ligament injuries can lead to arthritis years after the injury. They also may occur due to degenerative changes (age-related wear and tear). There isn’t a cure for RA but there are several treatment options including medications, reducing joint stress, physical and occupational therapy, and surgery. In rheumatoid arthritis, the synovial membrane that covers the knee joint begins to swell. Runner’s knee, also called patellar tendonitis, is one of the most common causes of knee pain in athletes.
Go to the ER if you can’t move your knee or leg, or if you think you have a broken bone. Let’s go over some of the questions that people with knee pain often ask doctors. Anyone who is experiencing persistent knee pain should see a doctor. Common problems include bone fractures, dislocated kneecaps, and torn ligaments.
They’re also responsible for the sensations you feel in your hips, leg, and ankle sensation. Pain from a deeper injury (called referred pain) can be passed along this nerve and felt on the surface. That means knee pain could arise from the knee itself or happen because of issues with your hip, ankle, or lower back. All of the sources of knee pain discussed below arise from the knee joint itself. Knee pain is so common that almost everyone’s felt it in their lives.
Doing the same repetitive motion (like jumping a lot, or working on your hands and knees) can cause knee pain. For example, you might feel pain when you’re moving or bending your knee which gets better when you rest. Some people also feel pain at different parts of the day. You could feel more pain first thing in the morning when you wake up. It’s also common to feel knee pain at night, especially if you were physically active earlier that day. The bursa are fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, muscles, and tendons in the joints.
Injury is one of the most frequent causes of chronic knee pain. This can include past trauma such as a torn ligament, meniscus tear, or dislocated kneecap. These injuries can lead to long-term pain and discomfort if not properly treated and rehabilitated.
Arthritis
Arthritis is another common culprit behind chronic knee pain. Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout can all contribute to inflammation and deterioration of the knee joint, leading to ongoing pain and stiffness.
Overuse
Overuse of the knee joint can also result in chronic pain. Activities that involve repetitive motions such as running, jumping, or squatting can put strain on the knee and lead to overuse injuries like patellar tendinitis or bursitis.
Obesity
Obesity is a significant risk factor for chronic knee pain. The extra weight puts added stress on the knee joints, which can accelerate wear and tear and lead to conditions like osteoarthritis.
Misalignment
Misalignment of the knee joint or poor biomechanics can also contribute to chronic knee pain. Issues with the alignment of the kneecap, leg length discrepancies, or muscle imbalances can all lead to ongoing discomfort in the knee.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the specific cause of your chronic knee pain and develop a treatment plan tailored to your needs.