Arthritis of the knee joint is a serious, painful disease that gets worse with age. Osteoarthritis is the most common type, and you can get it in one or both knees. The most common symptoms are pain, swelling and stiffness of the knee joint. There are many treatments that might help with the symptoms. When one or both pads of cartilage that cushion each of your knee joints deteriorates or tears, you may feel pain and a sticking or locking sensation.
It is weight training mixed with keeping your muscles limber. Cardio is important for keeping your weight stable and you feeling stronger overall. For cardio, some good choices include walking, swimming, water aerobics, stationary cycling, and elliptical machines. Tai chi may also help ease stiffness and improve balance. Too much rest can weaken your muscles, which can in turn increase reinjury. Find an exercise program that is safe for your knees and stick with it.
If you are one of the many individuals who suffer from chronic knee pain, you understand how debilitating it can be. Simple tasks like walking up stairs or bending down to pick something up can become excruciating when you have knee pain. Thankfully, there are several solutions available that can help alleviate your discomfort and improve your quality of life.
It’s also common to feel knee pain at night, especially if you were physically active earlier that day. Any knee pain that doesn’t improve despite home remedies and rest ought to be examined by a medical professional. These could be signs of a serious underlying cause, such as arthritis, an infection, or another related condition. Also known as septic arthritis or infectious arthritis, a joint infection may develop if a bacterial, viral, or fungal infection spreads to your joints.
Movement becomes restricted and pain gradually increases. A year-long study of 204 participants with knee osteoarthritis concluded that tai chi might have similar, if not greater, benefits compared with standard physical therapy. In 2014, researchers found that — rather than weather itself — sensitivity to weather in older people with osteoarthritis may affect how they experience joint pain. It should be wrapped in a cloth and applied for 20 minutes several times on the first day of injury. Never put ice directly the skin, as this can lead to further damage.
Exercise and Physical Therapy
One common reason for long-term knee pain is a type of arthritis known as osteoarthritis. It is thought to be caused by wear and tear in the joint. This article looks at exercises and stretches as part of a conditioning program to reduce knee pain.
The injection of the anesthetic drug for the nerve block is the test of whether RF ablation is likely to work. If the anesthetic relieved pain by 50% or more, even briefly, RF might be worth trying. Some people get immediate relief, but for most people it comes five to seven days later after the soreness and swelling subside. Like with a genicular nerve block, the procedure is done on an outpatient basis. It involves inserting a needle, the tip of which heats to about 176 F.
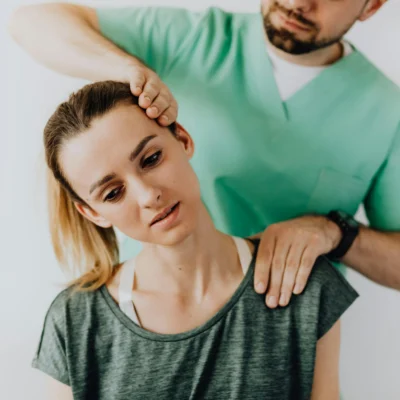
Exercise is a key component in managing knee pain. Strengthening the muscles around the knee can help provide support and stability, reducing strain on the joint itself. Physical therapy is also beneficial in teaching proper alignment and movement patterns to prevent further injury. Low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling can be particularly helpful for those with knee pain.
Braces and Supportive Devices
Wearing a brace or supportive device can help provide additional stability to the knee joint. These devices can help reduce pain and swelling by limiting movement and providing compression. There are a variety of braces available, so be sure to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best option for your specific needs.
Rest and Ice
When experiencing a flare-up of knee pain, it is important to give your body time to rest and recover. Icing the affected area can help reduce inflammation and numb the pain. Be sure to elevate your leg as well to further reduce swelling. Resting the knee and avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain can help promote healing.
By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can effectively manage your knee pain and improve your overall quality of life. Remember to consult with a healthcare provider before beginning any new treatment plan to ensure it is safe and appropriate for your individual needs.