Many people know patellofemoral syndrome as runner’s knee. Often, overuse is the main cause of pain, which tends to be around the kneecap. Typically, the pain is mild at first and gradually worsens over time. A person may experience a dull, aching pain that increases when going upstairs or bending the leg frequently. Treatment will depend on the type of injury, severity, and your overall health.
Several different things can lead to knee pain, and the treatments for it vary depending on what’s causing it. Knee pain is serious if you can’t bear weight on the knee, it causes severe pain, you hear a popping sound when it starts hurting, it looks deformed, or it swells suddenly. If you have any of these symptoms, contact your doctor and/or seek medical care right away.
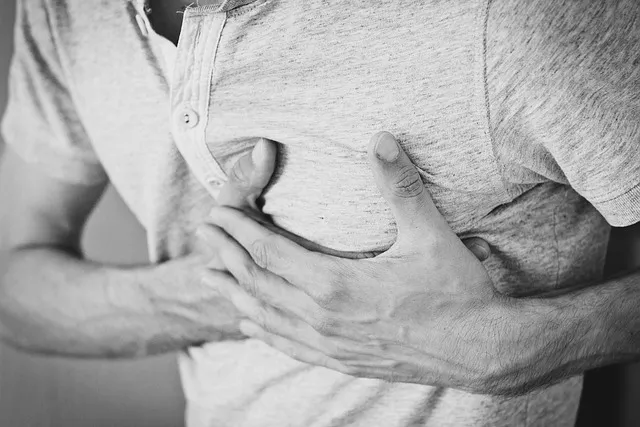
Knee pain is a common complaint among adults, affecting people of all ages and activity levels. Whether you are an athlete or someone who spends most of their day sitting at a desk, knee pain can be debilitating and impact your quality of life.
You may also hear it called “jumper’s knee” because repetitive jumping, such as from basketball, is the most common cause. If you’re dealing with symptoms of pain that won’t subside or a joint that locks up, don’t ignore them. If you’re experiencing severe knee pain, talk to your doctor to find out what’s causing it.
Yet despite one or more surgeries to “clean out the knee” – the pain lingers and persists. This ensures you’re doing the right exercises and stretches (and not making your knee pain worse). This is especially important if it has been longer than two to three days for swelling that isn’t reacting to OTC medication. The type of knee pain a person has when bending their leg depends on the cause. With osteoarthritis, for example, a person may experience general stiffness. With runner’s knee, they may feel more pain when walking upstairs.
Causes of Knee Pain
There are several reasons why you may be experiencing knee pain. One common cause is osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease that wears down the protective cartilage in your knee over time. Other causes include injuries such as ligament tears, tendonitis, bursitis, or meniscus tears. Overuse from repetitive movements or improper alignment can also lead to knee pain.
Many times, people will have the sensation of “catching” in the joint when they are active. Also known as septic arthritis or infectious arthritis, a joint infection may develop if a bacterial, viral, or fungal infection spreads to your joints. It most commonly develops in the knee joints, though the ankles, hips, and wrists are also sometimes affected. You may develop inner knee pain due to a health condition like osteoarthritis or a sudden injury. Sometimes, when and where the symptoms occur may help pinpoint the cause. There are several conditions that may cause inner knee pain without swelling, such as osteoarthritis (OA), medial meniscus injury, and medial plica irritation.
Treatment Options
“These 815 genes are rewiring the sensory nerves, which explains why anti-inflammatory drugs don’t work to alleviate pain for these patients,” Dr. Orange said. The findings may lead to new treatments for these outliers. Treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has come a long way in recent years. In many cases, a battery of medications can now successfully stymy the inflammatory cells that cause swelling and pain when they infiltrate tissues around the joints. If your knee hurts while bending your leg, take it easy. Home remedies like stretching or ice packs can also alleviate pain.
If you are experiencing knee pain, it is important to seek medical advice to determine the underlying cause. Treatment options may vary depending on the severity of your condition. In some cases, rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) may be recommended to reduce inflammation and pain. Physical therapy exercises can help strengthen the muscles around the knee for added support.
Surgical Interventions
In more severe cases, surgical interventions such as arthroscopic surgery or total knee replacement may be necessary to alleviate chronic knee pain. These procedures can help repair damaged tissues, realign the joint, or replace the knee joint altogether with a prosthetic device. Your healthcare provider will discuss the best treatment option for your specific condition.