Dealing with chronic knee pain can be debilitating and impact your quality of life. Finding the right treatment is crucial in managing and alleviating this discomfort. There are various options available depending on the cause and severity of the pain.
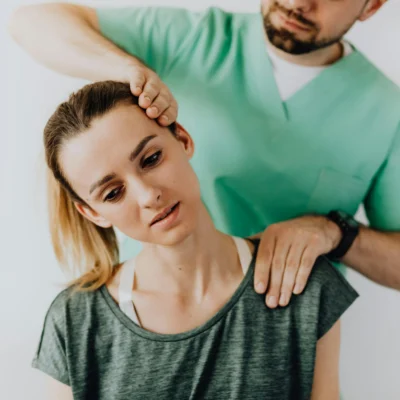
Physical Therapy
One common treatment for bad knee pain is physical therapy. A trained therapist can help you strengthen the muscles around your knee, improve flexibility, and correct any imbalances that may be contributing to the pain. Physical therapy can also help you learn proper techniques for movement to prevent further injury.
Medication
More than 90% of people who have gone through a knee replacement surgery told that they have a tremendous amount of relief in pain and their ability to walk around. The probability of positive outcomes hinges primarily on elements like the degree of injury, an individual’s general wellbeing, and compliance with recovery and subsequent care. Depending on your symptoms, your primary care provider may refer you to a variety of specialty doctors. For example, if they think it’s an injury, they may refer you to an orthopedist (a medical doctor who focuses on the musculoskeletal system). In some instances, your leg pain may go away on its own.
In some cases, over-the-counter or prescription medications may be recommended to manage knee pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Acetaminophen may also be used for pain relief.
The location of the pain can sometimes help a doctor diagnose the issue. If you have knee pain, you might be able to refer yourself directly to services for help with your condition without seeing a GP. It may take up to four weeks to notice any significant improvement, and the effects can vary from two to six months. Hyaluronic acid injections may be repeated about once every six months.
Injections
In addition to physical therapy, it’s critical to incorporate regular exercise into your daily routine. If you have overweight or obesity, the most effective treatment is weight loss. Every extra pound of weight adds two to four pounds of excess pressure on your knees. Make an appointment with a doctor if you still have pain after 2 weeks of home treatment, if the knee becomes warm, or if you have fever along with a painful, swollen knee. Aging, being overweight, and intense repetitive exercise can all cause knee pain.
If conservative treatments are not effective, your doctor may suggest injections such as corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid. Corticosteroid injections help reduce inflammation, while hyaluronic acid injections can help lubricate the joint and provide pain relief.
Go to the ER if you can’t move your knee or leg, or if you think you have a broken bone. Physiotherapy may help your knee pain, depending on what has caused it and what part of your knee hurts. A physiotherapist can give advice tailored to your individual situation. These might include physiotherapy, talking therapies and pain management programmes, surgery or injections.
Surgery
In severe cases where other treatments have failed, surgery may be necessary to address the underlying issue causing the knee pain. Procedures such as arthroscopic surgery, partial or total knee replacement, or realignment surgery may be considered based on your specific condition.
Unlike arthritis, bursitis tends to have a sudden and severe onset. You might also feel pain that extends beyond the affected joint. Arthritis refers to joint pain, stiffness, and inflammation. You can do many things to help knee pain, whether it’s due to a recent injury or arthritisyou’ve had for years. Go to the emergency room or call 911 (or your local emergency services number) if you’ve experienced a trauma like a car accident or severe fall.
The results of the study did not support the common belief that pain becomes worse in a colder climate. Study findings do not support this, although living in a pleasant climate might make pain psychologically easier. It may also provide easier opportunities to achieve a more healthy lifestyle. Elevation, or keeping the leg raised, will encourage circulation and reduce swelling. Ideally, the knee should be above the level of the heart.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medical interventions, making lifestyle changes can also help manage knee pain. Maintaining a healthy weight, staying active with low-impact exercises, and using supportive footwear can all contribute to reducing strain on your knees and preventing further pain.
Conclusion
Finding the right treatment for bad knee pain is essential in improving your quality of life and mobility. Working with your healthcare provider to determine the best approach for your individual needs can help you find relief and get back to doing the activities you enjoy.